What Are Scope 1, 2 and 3 Emissions and Why Are They Important?
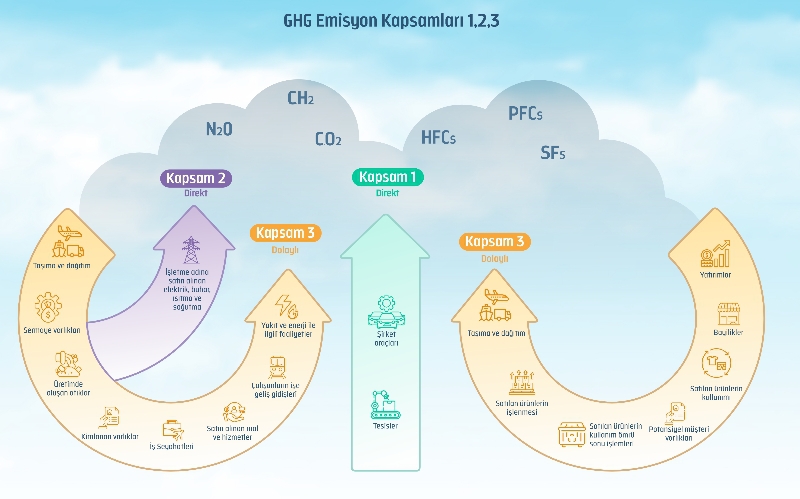
To combat climate change, companies and organizations need to measure and reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. One way to measure greenhouse gas emissions is to classify them as scope 1, 2 and 3.
Scope 1 Emissions
Scope 1 emissions are direct emissions from sources that a company owns or controls. This includes emissions from fuel used in buildings and manufacturing facilities, emissions from factory smoke, and emissions from refrigerant leaks.
Scope 2 Emissions
Scope 2 emissions are indirect emissions from the electricity, steam, heat and cooling a company purchases. This includes emissions from the production of electricity a company purchases, emissions from central heating or cooling systems a company uses, and emissions from refrigerants a company purchases.
Scope 3 Emissions
Scope 3 emissions are all other indirect emissions associated with a company's operations. This includes emissions from employees' commuting, emissions from business travel, emissions in the supply chain, and emissions from the use of the products and services a company produces.
If this is hard to grasp at first, we have a good acronym to remember what each scope includes: Scope 1 is what you burn;
Scope 2 is the energy you purchase;
Scope 3 is everything beyond this.
Why is it Important to Measure Scope Emissions?
Measuring scope emissions is critical to understanding a company's carbon footprint and impact. If a company wants to reduce its emissions, it must first measure them.
Measuring scope emissions allows a company to:
- Setting emission reduction targets
- Developing emission reduction strategies
- Monitor emissions reduction progress
- Assessing the impact of emissions reduction efforts
How to Measure Scope Emissions
Measuring scope emissions can be complicated depending on the company's operation and size. However, there are a variety of tools and methods that can be used to measure scope emissions.
Scope 1 and 2 emissions are generally relatively easy to measure. These emissions can be measured through fuel consumption, electricity bills and other measurements.
Scope 3 emissions may be more difficult to measure. To measure these emissions, it is necessary to understand the company's supply chain and product lifecycle.
Some tools and methods that can be used to measure scope emissions include:
- Greenhouse gas inventory software: This software offers a set of tools and functions that companies can use to measure their scope emissions.
- Calculators: A variety of scope emissions calculators are available on the internet. These calculators can help companies estimate scope emissions quickly and easily.
- Outsourcing: A company may outsource measuring scope emissions to a consultant or environmental consulting firm
As a result, measuring scope emissions is an important step in a company's efforts to combat climate change. By measuring scope emissions, a company can set emissions reduction targets, develop strategies, and track progress.



 Start Now
Start Now



